The Alaska Marine Highway, a lifeline for coastal communities, serves as a vital transportation network connecting remote villages, towns, and islands in Alaska. With its fleet of ferries, it provides essential access to healthcare, education, and economic opportunities while also facilitating tourism and recreation.
The system’s history dates back to the 1940s, and it has since expanded to include over 3,500 miles of routes along the Alaskan coastline. Today, the Alaska Marine Highway plays a crucial role in the economic and social fabric of the state, enabling the transportation of goods, supporting tourism, and fostering cultural exchange.
Alaska Marine Highway System

The Alaska Marine Highway System (AMHS) is a ferry system that provides vital transportation services to coastal communities in Alaska. It is operated by the Alaska Department of Transportation and Public Facilities (DOT&PF).
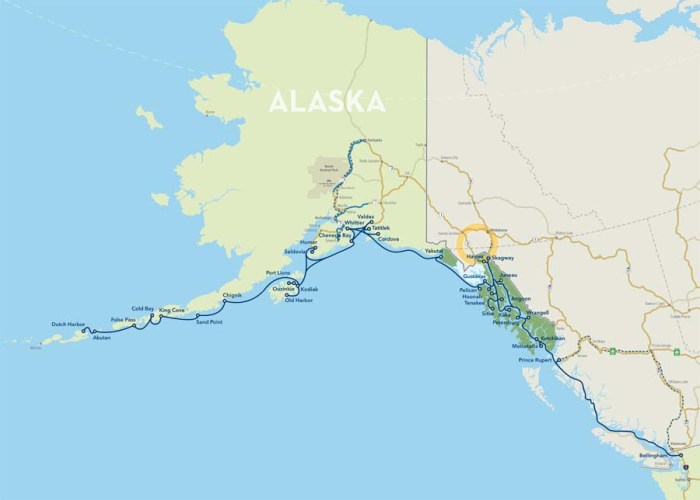
The AMHS was established in 1963 to connect isolated communities along Alaska’s vast coastline. Today, the system operates a fleet of 11 ferries that serve 35 communities in Southeast Alaska, the Gulf of Alaska, and the Aleutian Islands.
Routes and Vessels
The AMHS operates on several routes, including:
- Inside Passage: This route runs from Bellingham, Washington, to Skagway, Alaska, and includes stops in Ketchikan, Juneau, and Sitka.
- Gulf of Alaska: This route runs from Juneau to Cordova, Alaska, and includes stops in Valdez, Whittier, and Seward.
- Aleutian Islands: This route runs from Dutch Harbor to Unalaska, Alaska, and includes stops in Akutan, Atka, and Adak.
The AMHS fleet consists of a variety of vessels, including:
- Large ferries: These ferries are over 400 feet long and can carry up to 500 passengers and 150 vehicles.
- Medium ferries: These ferries are between 250 and 350 feet long and can carry up to 300 passengers and 100 vehicles.
- Small ferries: These ferries are under 250 feet long and can carry up to 100 passengers and 50 vehicles.
Communities Served
The AMHS serves a wide range of communities, from small villages to large cities. These communities rely on the ferry system for transportation, commerce, and tourism.
- Ketchikan: A major port city in Southeast Alaska, Ketchikan is a popular tourist destination.
- Juneau: The capital of Alaska, Juneau is a major transportation hub and a popular cruise ship destination.
- Sitka: A historic city in Southeast Alaska, Sitka is known for its Russian architecture and totem poles.
- Cordova: A small city in the Gulf of Alaska, Cordova is a popular destination for fishing and kayaking.
- Valdez: A port city in the Gulf of Alaska, Valdez is the terminus of the Trans-Alaska Pipeline.
- Seward: A small city in the Gulf of Alaska, Seward is a popular gateway to Kenai Fjords National Park.
- Dutch Harbor: A major fishing port in the Aleutian Islands, Dutch Harbor is the home of the largest seafood processing plant in the United States.
- Unalaska: A small city in the Aleutian Islands, Unalaska is a major fishing and seafood processing center.
The AMHS is a vital part of the transportation infrastructure in Alaska. It provides essential services to coastal communities and supports the state’s economy.
Economic and Social Impacts
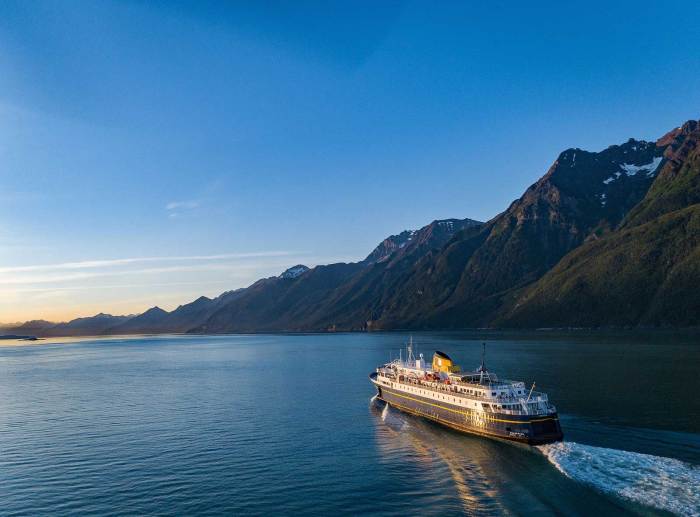

The Alaska Marine Highway System has significant economic and social impacts on the state of Alaska. These impacts include:
Tourism
- The Alaska Marine Highway System is a major tourist attraction, with over 1 million passengers traveling on the ferries each year.
- Tourists spend money on accommodations, food, and activities in the communities that the ferries serve.
- The tourism industry supports jobs and businesses in these communities.
Transportation of Goods
- The Alaska Marine Highway System is a vital transportation link for communities that are not connected to the road system.
- The ferries transport goods such as food, fuel, and building materials to these communities.
- The transportation of goods helps to keep the cost of living in these communities affordable.
Access to Remote Communities
- The Alaska Marine Highway System provides access to remote communities that are not accessible by road.
- This access allows residents of these communities to travel to other parts of the state for medical care, education, and other services.
- The ferries also transport goods and supplies to these communities, which helps to improve their quality of life.
Improved Connectivity
- The Alaska Marine Highway System connects communities in Alaska to each other and to the rest of the United States.
- This connectivity allows people to travel for business, leisure, and education.
- The ferries also provide a way for people to connect with their families and friends who live in different parts of the state.
Healthcare Access
- The Alaska Marine Highway System provides access to healthcare for residents of remote communities.
- The ferries transport patients to medical facilities in larger communities.
- The ferries also provide telemedicine services, which allow patients to receive medical care from a distance.
Cultural Exchange
- The Alaska Marine Highway System facilitates cultural exchange between different communities in Alaska.
- The ferries transport people from different cultures and backgrounds to different parts of the state.
- This interaction helps to promote understanding and appreciation of different cultures.
Environmental Considerations: Alaska Marine Highway
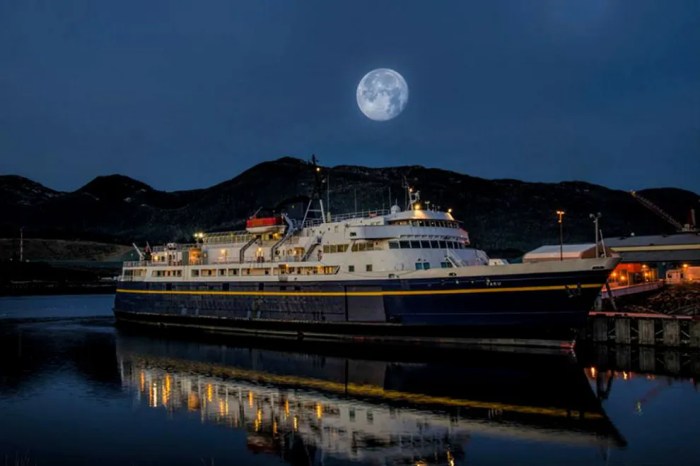

The Alaska Marine Highway System has potential environmental impacts that need to be considered and mitigated. These include emissions, noise pollution, and habitat disturbance.
The Alaska Marine Highway, a scenic ferry system, transports passengers and vehicles through breathtaking landscapes. From the Inside Passage to the remote islands of Southeast Alaska, it offers a unique perspective on the region’s natural beauty. Along the way, it passes by historic sites such as Alnwick Castle , a magnificent medieval fortress in England.
The castle’s stunning architecture and fascinating history add to the allure of the Alaska Marine Highway’s journey, connecting the rugged wilderness of Alaska with the grandeur of ancient Europe.
Emissions from the ferries include air pollutants such as nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, and particulate matter. These emissions can contribute to air quality problems in coastal communities and can also affect the health of marine life. The ferries also produce noise pollution, which can disturb marine mammals and other wildlife.
Mitigation Measures
The Alaska Marine Highway System has taken several measures to mitigate its environmental impacts. These include:
- Using cleaner-burning fuels
- Installing emissions control devices
- Reducing ferry speeds in sensitive areas
- Educating passengers and crew about environmental protection
These measures have helped to reduce the environmental impacts of the Alaska Marine Highway System. However, there is still more that can be done to improve sustainability.
Tourism and Recreation
The Alaska Marine Highway System (AMHS) serves as a vital gateway to some of Alaska’s most breathtaking destinations, playing a pivotal role in promoting tourism and recreation throughout the state. With its network of ferries connecting coastal communities and remote islands, the AMHS offers travelers unparalleled access to pristine wilderness areas, abundant wildlife, and a wide range of outdoor activities.
One of the key highlights of the AMHS is its access to popular tourist destinations. Juneau, the state capital, boasts a vibrant downtown area with museums, art galleries, and historical sites. Skagway, a historic gold rush town, offers a glimpse into Alaska’s colorful past. Ketchikan, known as the “Salmon Capital of the World,” provides opportunities for fishing and wildlife viewing. These destinations are just a few examples of the many alluring places accessible via the AMHS.
Wildlife Viewing, Alaska marine highway
The AMHS is renowned for its exceptional wildlife viewing opportunities. Passengers can often spot whales, dolphins, sea lions, and otters along the ferry routes. The Inside Passage, in particular, is a renowned whale-watching destination, with humpback whales, orcas, and gray whales frequently sighted. Bald eagles, puffins, and other seabirds are also common sights, providing ample opportunities for birdwatching enthusiasts.
Whether you’re planning a relaxing beach holiday or an adventurous journey along the Alaska Marine Highway, packing the right items is crucial. For beach essentials, refer to the comprehensive beach holiday packing list for a detailed guide. Once you’ve got your beachwear and sun protection sorted, don’t forget to consider the unique requirements of the Alaska Marine Highway, such as warm clothing, comfortable footwear, and entertainment options for the scenic voyage.
Adventure Activities
The AMHS also serves as a gateway to various adventure activities. Many destinations along the ferry routes offer opportunities for hiking, kayaking, fishing, and camping. The Inside Passage, with its protected waters and stunning scenery, is ideal for kayaking and whale watching. The remote islands and inlets provide secluded spots for camping and fishing, allowing visitors to immerse themselves in the pristine wilderness.
The Alaska Marine Highway offers an unforgettable journey through breathtaking landscapes. For those seeking an elevated experience, luxury travel deals provide access to exclusive amenities and personalized services. Immerse yourself in the pristine wilderness while enjoying the comforts of a luxurious cabin or suite.
As the ferry sails along the scenic coastline, embrace the tranquility and immerse yourself in the natural beauty that surrounds you.
Challenges and Future Prospects
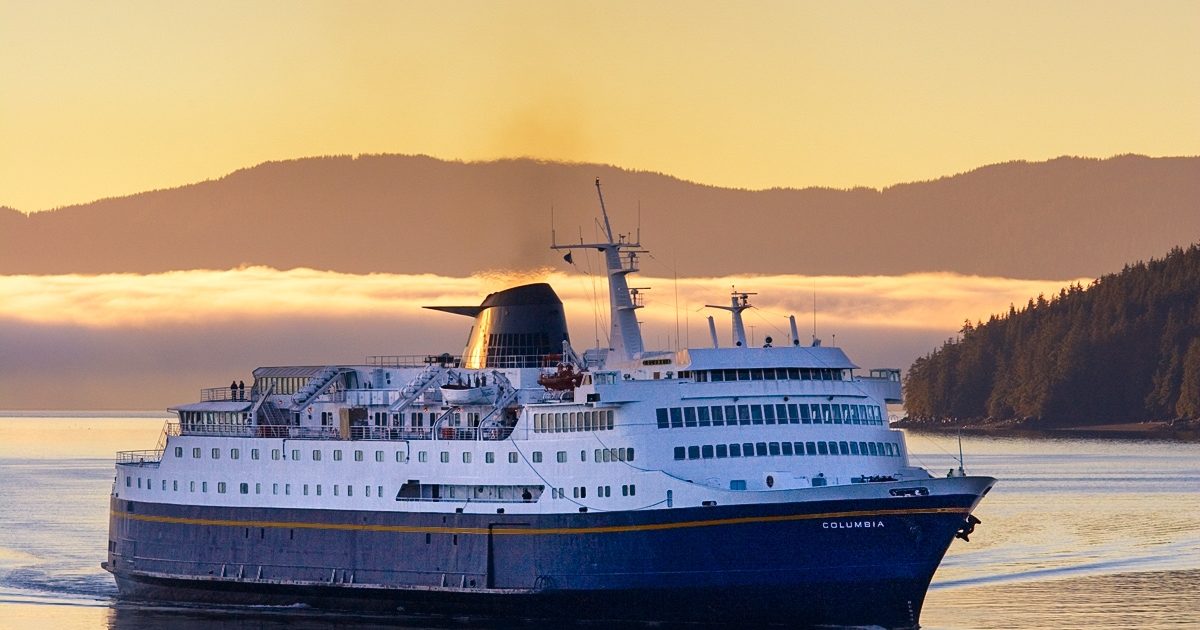

The Alaska Marine Highway System faces several challenges, including funding, infrastructure maintenance, and seasonal limitations. Funding for the system has been declining in recent years, making it difficult to maintain and improve infrastructure. Additionally, the system’s infrastructure is aging and in need of repairs and upgrades. Finally, the system is only operational during the summer months, which limits its use for year-round transportation.
There are several potential solutions to these challenges. To address funding issues, the state could increase its investment in the system or seek federal funding. To improve infrastructure, the state could invest in new ferries and terminals. To extend the system’s operational season, the state could invest in ice-breaking technology.
In addition to these challenges, the Alaska Marine Highway System also has several future prospects. The system could be expanded to new communities, and new ferry routes could be added. The system could also be used to transport goods and materials, in addition to passengers. Finally, the system could be used to promote tourism and recreation in Alaska.
Funding
Funding for the Alaska Marine Highway System has been declining in recent years. In 2015, the state legislature cut funding for the system by $10 million. This cut has made it difficult to maintain and improve the system’s infrastructure.
There are several potential solutions to the funding challenges facing the Alaska Marine Highway System. One solution is to increase the state’s investment in the system. The state could also seek federal funding for the system.
Infrastructure Maintenance
The Alaska Marine Highway System’s infrastructure is aging and in need of repairs and upgrades. Many of the ferries in the system are over 30 years old and are in need of replacement. Additionally, many of the terminals in the system are in need of repairs and upgrades.
There are several potential solutions to the infrastructure maintenance challenges facing the Alaska Marine Highway System. One solution is to invest in new ferries and terminals. The state could also seek federal funding for infrastructure improvements.
Seasonal Limitations
The Alaska Marine Highway System is only operational during the summer months. This limits the system’s use for year-round transportation.
There are several potential solutions to the seasonal limitations facing the Alaska Marine Highway System. One solution is to invest in ice-breaking technology. This would allow the system to operate during the winter months.
Closure
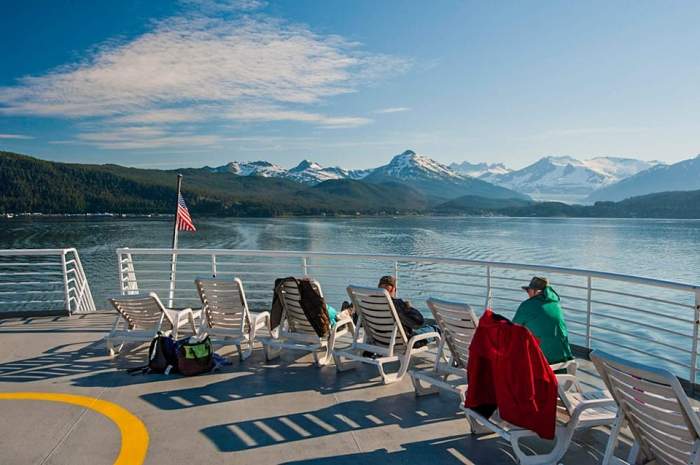

The Alaska Marine Highway stands as a testament to the ingenuity and resilience of the Alaskan people. It not only connects communities but also serves as a catalyst for economic growth and cultural preservation. As the state continues to evolve, the Alaska Marine Highway will undoubtedly remain a vital lifeline, ensuring the well-being and prosperity of coastal communities for generations to come.
Detailed FAQs
What is the purpose of the Alaska Marine Highway?
The Alaska Marine Highway serves as a vital transportation network, connecting remote coastal communities and providing access to essential services, goods, and tourism opportunities.
What is the history of the Alaska Marine Highway?
The Alaska Marine Highway’s origins can be traced back to the 1940s, and it has since expanded to become a comprehensive ferry system serving over 3,500 miles of coastline.
What are the economic benefits of the Alaska Marine Highway?
The Alaska Marine Highway contributes to economic growth by supporting tourism, facilitating the transportation of goods, and providing access to resources for remote communities.
What are the social impacts of the Alaska Marine Highway?
The Alaska Marine Highway fosters social connectivity, improves access to healthcare and education, and facilitates cultural exchange among coastal communities.
What are the environmental considerations related to the Alaska Marine Highway?
The Alaska Marine Highway is committed to minimizing environmental impacts through measures such as reducing emissions, mitigating noise pollution, and protecting marine habitats.